Types of Foundation Crack Repair Methods
Foundation Crack Repair Methods: Find Reliable Washington DC Contractors for Expert Solutions
Foundation cracks are a common problem faced by homeowners, especially in regions where extreme weather fluctuations occur. Cracks in a foundation can be alarming, but not all cracks are the same, and the type of crack determines the best repair method. Depending on the severity and cause of the crack, different foundation repair methods can be used to ensure the structure's stability and prevent future damage. If you're searching for "foundation repair near me," particularly for "foundation repair Washington DC," it's important to understand the available repair techniques, especially when considering "Washington DC contractors" who specialize in foundation repairs. This guide will help you understand the types of foundation crack repair methods and which might be most suitable for your home.

Understanding Foundation Cracks
Before diving into the different repair methods, it's essential to identify the type of foundation cracks that can appear:
1. Hairline Cracks
These are minor, superficial cracks, often caused by normal concrete shrinkage as it cures. Hairline cracks are not usually a sign of serious structural problems but should still be monitored.
2. Vertical Cracks
Vertical cracks are the most common type and often result from normal foundation settling. They may not pose an immediate threat, but if left unattended, they can worsen over time.
3. Horizontal Cracks
Horizontal cracks indicate more serious issues. They typically result from soil pressure or water buildup around the foundation, which can lead to foundation movement or bowing walls. Horizontal cracks should be addressed promptly to prevent further structural damage.
4. Diagonal Cracks
Diagonal cracks usually occur due to uneven settlement of the foundation. These cracks can indicate that one part of the foundation is sinking more than another, causing stress on the structure.
5. Stair-Step Cracks
Stair-step cracks are often seen in brick or concrete block foundations. They resemble a staircase and typically signal differential settlement in the foundation.
Foundation Crack Repair Methods
When it comes to repairing foundation cracks, the type of crack and the underlying cause must be taken into account. The most common repair methods include:
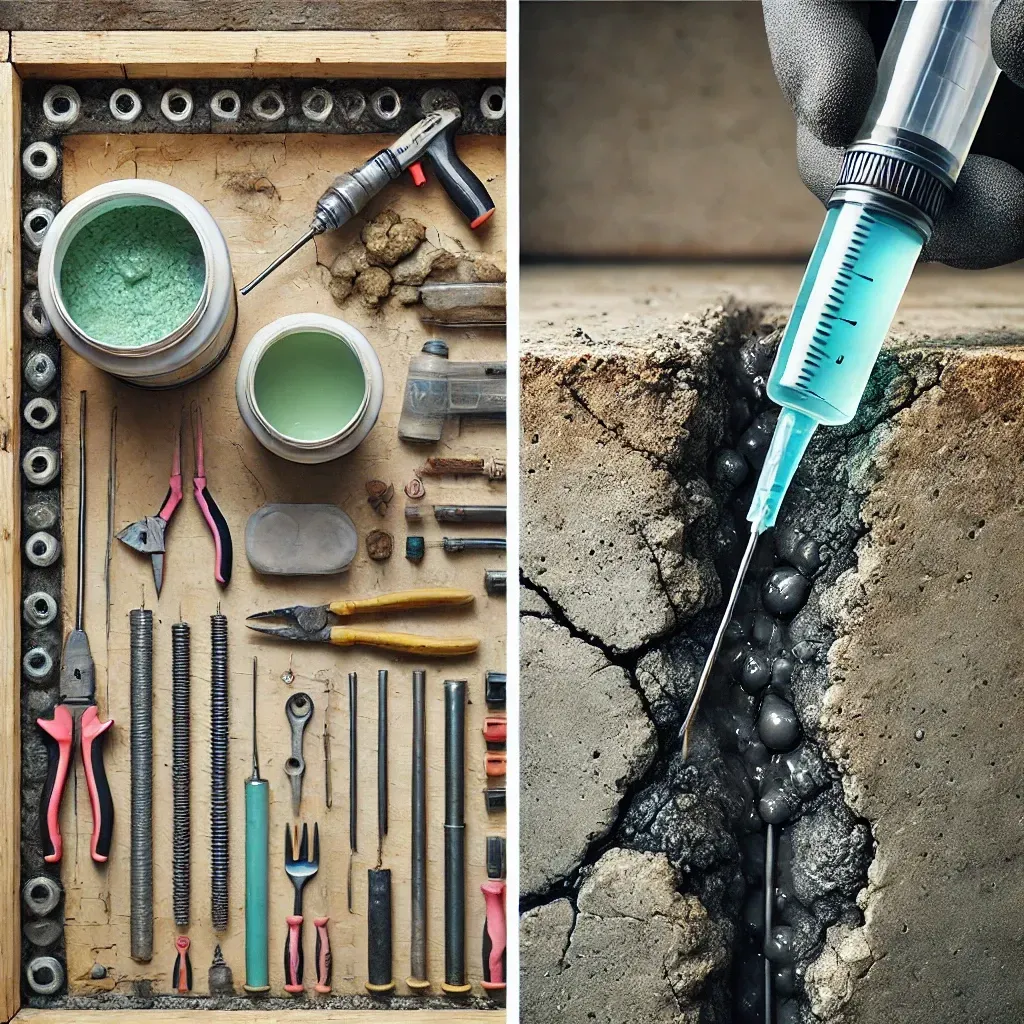
1. Epoxy Injection
Epoxy injection is a popular solution for repairing small to medium-sized cracks, particularly vertical cracks. This method involves injecting a high-strength epoxy resin into the crack. The epoxy bonds the crack together, restoring the structural integrity of the foundation.
How It Works:
- The crack is first cleaned, and any debris is removed.
- Ports are installed along the crack to allow the epoxy to be injected.
- Epoxy is injected under pressure, filling the entire crack.
- Once the epoxy cures, it forms a strong bond, preventing further movement.
Pros:
- Effective for small to medium cracks.
- Restores the foundation's structural strength.
- Fast and cost-effective.
Cons:
- Not suitable for active cracks or cracks caused by structural movement.
- Requires a professional for proper application.
2. Polyurethane Foam Injection
Polyurethane foam injection is similar to epoxy injection but is often used for cracks that are leaking or where water infiltration is a concern. The polyurethane foam expands once injected into the crack, sealing it off from moisture and preventing further water damage.
How It Works:
- The crack is cleaned, and injection ports are installed.
- Polyurethane foam is injected under pressure, where it expands to fill the crack.
- The foam cures quickly, forming a waterproof seal.
Pros:
- Ideal for sealing leaking cracks.
- Quick curing time.
- Expands to fill larger cracks.
Cons:
- Not as strong as epoxy for structural repairs.
- Best for non-structural, water-related issues.
3. Carbon Fiber Straps
For more severe cracks, particularly horizontal and stair-step cracks that indicate bowing walls or foundation movement, carbon fiber straps may be used. Carbon fiber is extremely strong and lightweight, and these straps can stabilize the foundation wall without requiring extensive excavation.
How It Works:
- The wall is prepared by cleaning and smoothing the surface around the crack.
- Epoxy is applied to the wall, and carbon fiber straps are pressed into place over the crack.
- The straps bond with the epoxy and reinforce the wall, preventing further movement.
Pros:
- Non-invasive repair method.
- No need for excavation.
- Extremely strong and durable.
Cons:
- Best for preventing further movement, not for fixing existing damage.
- Only suitable for certain types of cracks, such as bowing walls.
4. Steel Piering
Steel piering is a more invasive method used for significant foundation settlement issues. It involves driving steel piers deep into the ground beneath the foundation to reach stable soil or bedrock. These piers are then used to lift and stabilize the foundation.
How It Works:
- Steel piers are driven into the ground below the foundation.
- The foundation is lifted back to its original position.
- The piers provide long-term stability, preventing future settlement.
Pros:
- Provides permanent stabilization.
- Can lift the foundation back to its original position.
Cons:
- Expensive and invasive.
- Requires heavy machinery and skilled professionals.
5. Helical Piers
Helical piers work similarly to steel piers but are designed with screw-like helices that allow them to be twisted into the ground. These piers are often used in areas where soil conditions are challenging, such as in the Washington DC area, where clay or sandy soils are common.
How It Works:
- Helical piers are screwed into the ground until they reach stable soil or bedrock.
- The foundation is lifted and stabilized using the piers.
Pros:
- Suitable for challenging soil conditions.
- Provides permanent stabilization.
Cons:
- Can be expensive and invasive.
- Requires professional installation.
6. Slab Jacking
Slab jacking, also known as mud jacking, is a method used to lift sunken concrete slabs. This technique is often used for foundations with slab-on-grade construction. A mixture of cement, sand, and other materials is pumped under the slab to lift it back into place.
How It Works:
- Small holes are drilled into the sunken slab.
- A mixture of materials is pumped into the holes, filling the void beneath the slab and lifting it.
- The holes are patched, and the slab is restored.
Pros:
- Less invasive than other methods.
- Cost-effective.
Cons:
- Not suitable for severe settlement issues.
- May not provide long-term stabilization for certain soil types.
Choosing the Right Foundation Repair Method
Selecting the right foundation crack repair method depends on several factors, including the type of crack, the cause of the crack, and the condition of the surrounding soil. If you're searching for "foundation repair near me" or "Washington DC foundation repair," it's important to consult with professional "Washington DC contractors" who can assess your foundation and recommend the best solution.
For minor cracks, epoxy or polyurethane foam injection may be sufficient, while more serious structural issues may require carbon fiber straps, steel piers, or helical piers. It's essential to address foundation cracks as soon as they appear to prevent further damage and avoid costly repairs down the line.